COMMUNITY OUTREACH
Sample Activity Description

Sample Activity in Action
RESEARCH FINDINGS
Method
All students were given a pre-test which consisted of two tasks that assessed social and emotional competencies. Students in the experimental condition received 14 lessons taught by San Francisco State University psychology students who partnered with Chinese teachers and translators. The lessons focused on four key areas of SEL: emotion identification and awareness, self-management and coping, self-awareness and perspective taking, and social skills and pro-social behaviors. Students in the control condition did not receive our curriculum and solely received typical classroom instruction. Upon the completion of the SEL program, all students were given a post-test that was identical to the pre-test. Performance scores on the social and emotional tasks were compared between the experimental and control conditions for pre- and post-tests.
Results
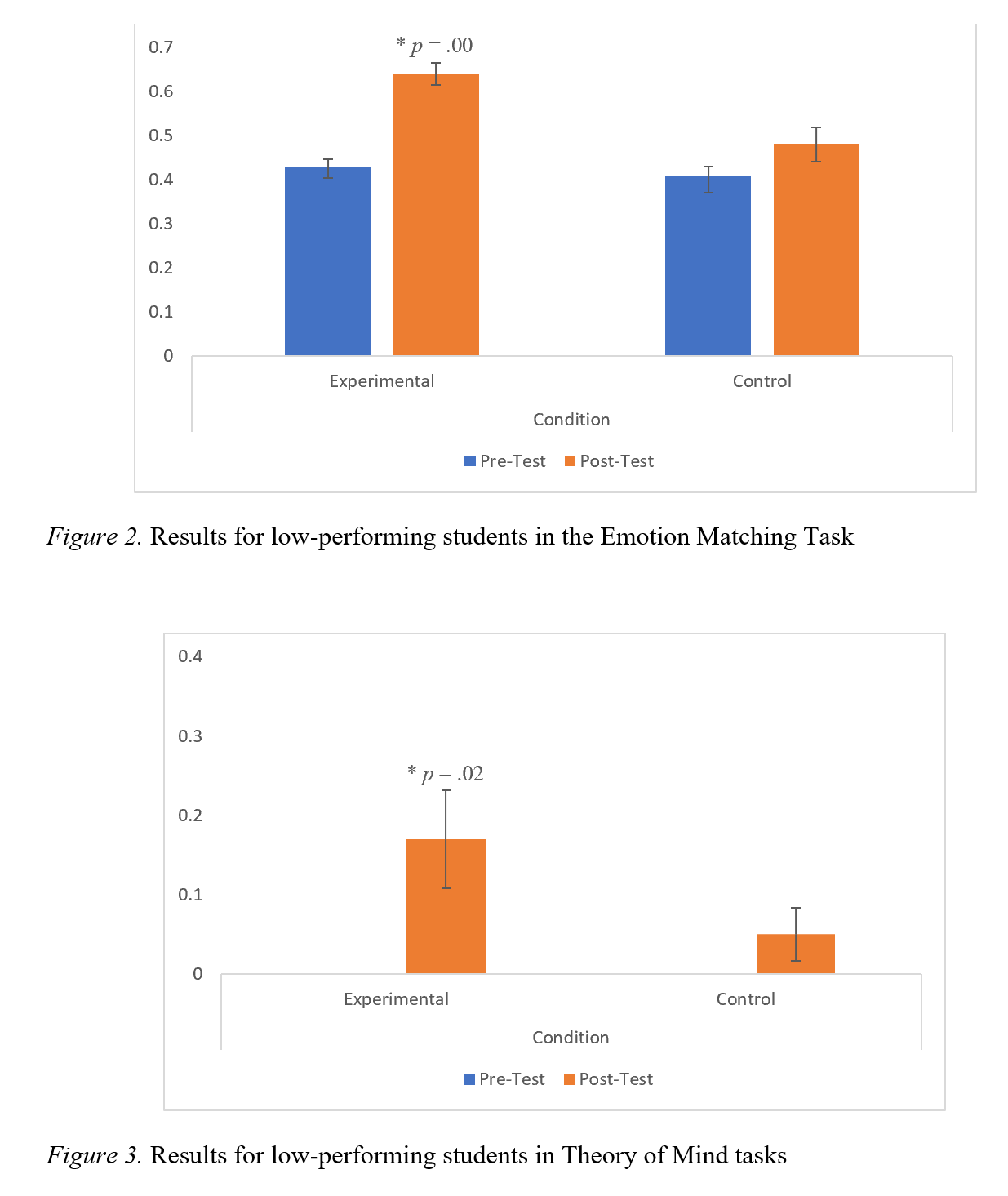
Regarding emotion knowledge, consistent with our prediction as well as previous findings, a significant increase in student performance was found as a result of the SEL training program. Taking a closer look, we found that initially low-performing students (i.e., those who scored fewer than 6 out of 8 on the EMT task) were driving the improvement in scores for the experimental condition, showing an increased benefit for previously underperforming students. As expected, no such increase in competency was found in the control condition, regardless of initial performance.
Unlike emotion knowledge, when accounting for all students, ToM understanding did not show significant improvement as a result of the SEL training program. However, when measuring initially low-performing students (i.e., those who scored 0 on both ToM tasks), a significant increase did occur showing an increased benefit for previously underperforming students. As expected, no such increase in competency was found in the control condition.
Overall, the present findings are consistent with our hypotheses, as the current program did have a positive impact on students’ emotion knowledge and ToM understanding, though the benefits may be limited to initially underperforming students by helping them rise closer to their peers in social and emotional competencies.